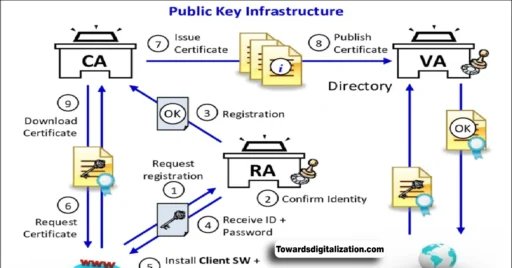
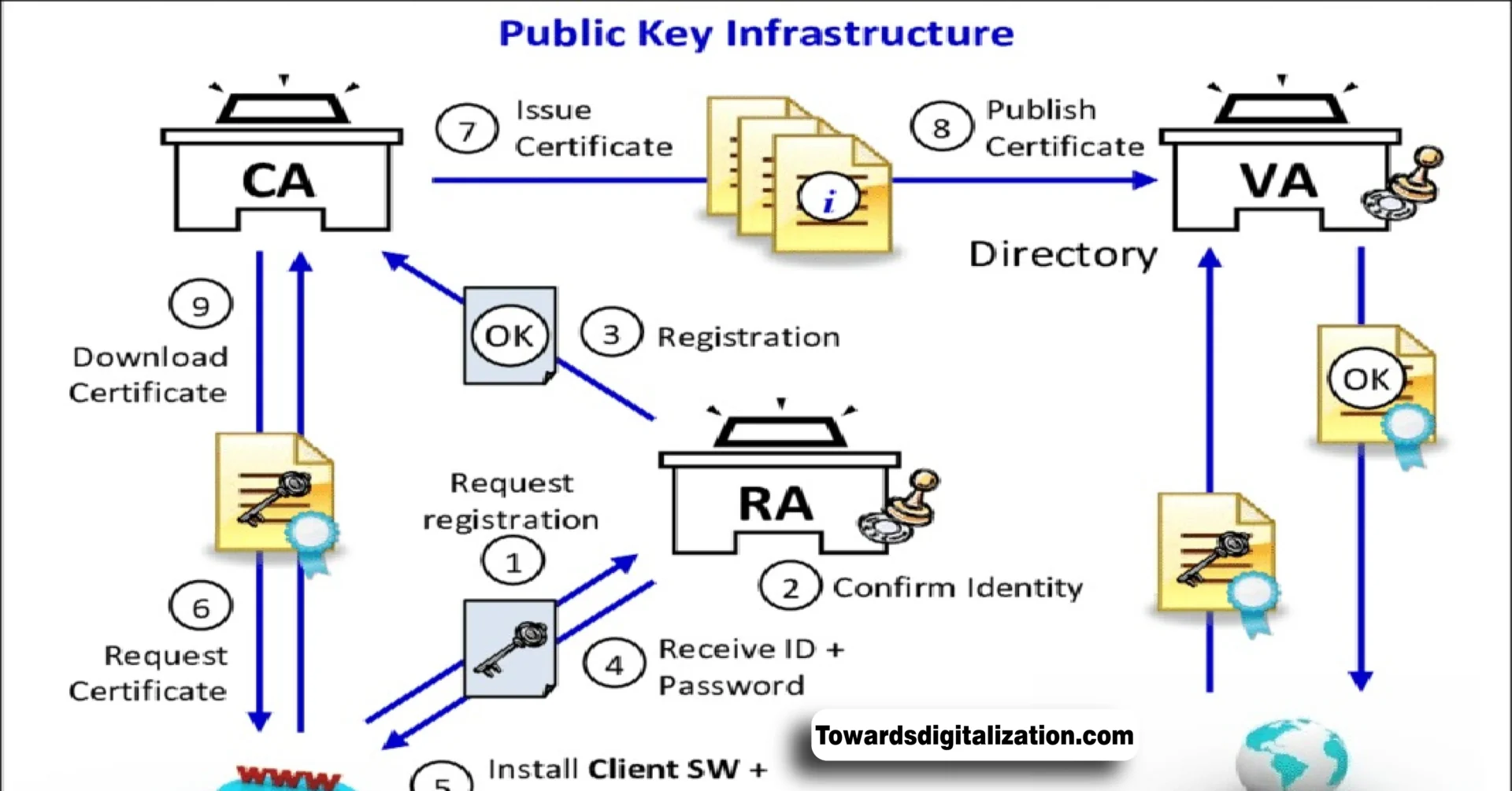
Introduction
A Policy for Certification of Application Deployment provides guidelines, procedures, and standards needed to ensure software apps are used safely, efficiently, and compliantly. Its aim is to make sure each deployment fulfills organizational requirements that mitigate risks while guaranteeing stable operations.When Application Deployment Certification Policy comes to software application deployment, having a reliable and safe process is vitally important to business.
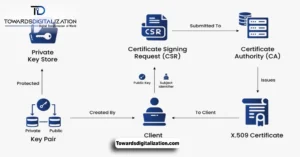
A certification policy for application deployment provides not only guidelines but a way of guaranteeing smooth deployments while upholding high-quality operations. If you’re an organization looking to standardize app deployment procedures or an IT professional responsible for overseeing them, understanding these policies of certification will improve processes while mitigating risks.
This blog explored the basics of certification for deployment policies and their significance for businesses, while offering practical guidelines on how to create one successfully. By the end of this blog post you’ll understand their value to your enterprise and how best to utilize them to your advantage.
Why Are Application Deployment Certification Policy?
1. Quality Assurance
A certification policy mandates rigorous testing of your software and updates in all environments intended for them, to eliminate errors after deployment which could disrupt users or business processes. This helps eliminate mistakes which arise post deployment that might cause disruptions or errors for users or processes.
2. Enhance Security Measures Application Deployment Certification Policy
Certified deployments feature extensive checks for potential security flaws. Given how costly security breaches are around the world, ensuring security in deployment is no longer optional but rather essential.
3. Maintain Consistency Application Deployment Certification Policy
Certification policies provide the framework for consistent, repeatable processes regardless of project complexity or the person leading implementation, providing predictable results while decreasing human errors. This ensures greater predictability with less chance for human mistakes.
4. Simplifying Communication and Accountability Application Deployment Certification Policy
A deployment certification policy helps large groups streamline communication and accountability by outlining roles and obligations, so everyone from testers to engineers knows exactly their responsibilities.
5. Conformance to Regulations Application Deployment Certification Policy
Your industry and company type dictate how to create policies to stay compliant with frameworks like ISO 27001 or GDPR, so make sure yours have them.
Key Purposes of Application Deployment Certification Policy
1. Guaranteeing Security Compliance
Applications have access to sensitive company data. Therefore, this policy seeks to ensure that any software accessing such information complies with data protection laws such as GDPR or HIPAA prior to being deployed into use.
2. Maintaining Functional Integrity
The policy ensures that applications work as intended, thus preventing glitches or crashes from disrupting business processes.
3. Maintaining Standardization
A policy designed to standardize application deployment will create an orderly and flexible method. This ensures that software meets both technical and business standards imposed by your organization – such as code practices or protocols for integration.
4. Risk Mitigation
By addressing potential vulnerabilities during certification processes, this program reduces the chance that applications installed may disrupt processes, compromise systems or facilitate cyberattacks.
5. Strengthen Stakeholder Confidence
Launching an app with strong certifications shows a commitment to quality and security, building trust among employees, customers, partners and other stakeholders.
Core Components of an Application Deployment Certification Policy
A strong policy must include components that make it both actionable and adaptable across organizations. To be truly effective, policies must contain these essential pieces that ensure effective outcomes.
1. Pre-Deployment Testing Steps
Before an application can go live, it must undergo extensive pre-deployment tests, including functional, integration, and performance evaluations to ensure it functions as expected under all possible scenarios.
2. Security Audits
These audits aim to uncover vulnerabilities while verifying compliance with data protection regulations, protecting sensitive information. Automated tools such as OWASP ZAP and Nessus will accelerate security testing efforts.
3. Documentation and Approval Workflow
It is vitally important that tests, application specifications, risk analyses and approval decisions are meticulously recorded and adhere to predefined success criteria.
4. Establish Metrics and Benchmarks
By setting benchmarks — such as maximum allowable downtime, minimum throughput capacity or acceptable error rates – it becomes easier to ascertain whether an application meets your organization’s quality standards.
1. Objective
Purpose Application Deployment Certification Policy:
The purpose of this policy is to ensure only compliant, secure and functional applications are installed in the workplace.
Goals Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Our goals include minimizing operational risk while strengthening security measures and assuring all applications conform with high quality standards.
2. Scope About Application Deployment Certification Policy
Covered Applications:
This definition covers an assortment of internal and third-party applications deployed in production environments – including cloud-based, on-premises, hybrid solutions.
Deployment Environments:
Development Environments define the environment where applications will be installed (e.g. production, development or stage).
Stakeholders:
Stakeholders include developers, IT operations teams, security teams and quality assurance (QA) teams as well as any other relevant individuals.
3. Certification Criteria
The policy will establish guidelines for certifying applications prior to deployment, including evaluation criteria in various areas such as:
Security:
The application does not present any vulnerabilities and adheres to security guidelines (e.g. encryption or authentication and protection of data), and has successfully passed appropriate penetration tests.
Compliance Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Conforming to regulatory and legally mandated requirements (e.g. GDPR, HIPAA and PCI DSS).
Performance Evaluating application performance against capacity, load and response time benchmarks.
Integration Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Checking the compatibility of an application with existing platforms and infrastructure.
Usability and Functionality Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Tests Ascertaining whether an app meets users’ expectations as set by stakeholders community.
Documentation:
Checking that user manuals, support documents and specifications related to technical aspects are available is key in the Certification Process.
4. Certification Process Application Deployment Certification Policy
The Initial Evaluation: It begins by performing an initial analysis of an application’s requirements, architecture and design.
Evaluation and Validation: The application undergoes multiple tests, such as security, functional, and performance verification.
Code review: A comprehensive analysis of an application’s codebase in order to detect security weaknesses, inefficiencies and compliance issues with best practices.
Approval Process: An approval procedure provides stakeholders from IT teams, security and operations teams and business representatives an opportunity to review and approve an application prior to its deployment.
Sign-off: Receiving approval from authorized individuals or committees (e.g., IT Governance Board).
5. Handling of Exceptions Application Deployment Certification Policy
Conditions for exceptions: If an application cannot meet certification requirements, an explicit procedure should exist for requesting exceptions – mitigating controls or staged deployment could provide some form of mitigation.
Mitigation: Deliberately selecting mitigations that address risks arising from the program use.
6. Roles and Responsibilities Application Deployment Certification Policy
Development Team: Developer Team imunitar is accountable for ensuring its application complies with standards, providing documentation to support it, and meeting regulatory compliance.
Security Team: Conducting Security Audits and Assessments.
Quality Assurance (QA) Team: Conducted Functional and Performance tests as well as user Acceptance Testing (UAT).
IT Operations Team: Oversaw deployment processes while monitoring post-deployment performance as well as overseeing troubleshooting efforts.
Compliance Officer: Compliance Officer/Authorized Official is responsible for assuring compliance with any applicable rules or Internal policies.
Approval Authority: Aproval Authority/Committee are charged with the final approval process.
7. Deployment Strategy
Deployment Method: Define whether deployment will be manual or automated (such as pipelines for continuous integration/continuous delivery).
Rollback Procedures: With specific roll back procedures available should problems arise during implementation.
Regular Monitoring: To ensure the application is functioning as intended post deployment and identify any potential issues quickly, it is vital that monitoring be conducted on an ongoing basis.
8. Training and Awareness Application Deployment Certification Policy
Training for Teams: Training all relevant participants (such as IT developers and IT operation) on certification policies and best practices for deployment.
Users Awareness: Users’ awareness is ensured of any new features or modifications to work processes that affect them, while remaining informed.
9. Documentation and Reporting Application Deployment Certification Policy
Audit logs: Audit logs record in detail the certification process, approvals, and any exceptions or deviations for accountability and future audits.
Certification reports: Reports that present findings achieved through accreditation processes, including any risks identified and mitigation strategies implemented.
After-Deployment Evaluation: An evaluation of the deployment to identify any lessons that can be learned.
10. Review and Update of Policy
Continuous improvement: The policy must be evaluated regularly to make sure it aligns with new technologies, security threats and regulations for compliance; while also meeting organizational needs.
Feedback Loops: Collect feedback from teams participating in the certification process in order to facilitate future deployments and enhance them.
Key Takeaways
An App Deployment Certification Policy ensures that applications comply with security regulations and performance criteria before being deployed into production environments. Firstly, it is essential to clarify certification requirements, approval processes, and roles and obligations. Additionally, documentation requirements must be well-defined to avoid ambiguity. Moreover, attention should be given to handling exceptions and developing risk mitigation strategies. Finally, addressing post-deployment monitoring issues is crucial to ensure ongoing compliance and performance.
This policy helps reduce deployment risks, enhance application quality and comply with organizational standards throughout deployment’s lifecycle.
Roles and Responsibilities
Application Deployment Team:
The Team for Application Deployment is responsible for overseeing deployment as well as ensuring applications meet certification standards.
IT Security Team: IT Security Team is responsible for conducting an assessment on each application prior to its deployment.
Quality Assurance (QA) Team:
The team ensures that software has passed all tests of quality assurance.
Compliance and Risk team:
They verify that an application complies with legal, regulatory, and compliance requirements within an organization.
Development Team:
They ensure that their application meets Coding and performance standards.
End users:
Provide feedback after deployment of an application and report any operational problems that may occur.
Key Components of a Strong Certification Policy
An Effective Certification Policy An effective deployment certification policy can bridge the divide between quality assurance, development and operations teams. Here are the core elements each policy should contain:
1. Pre-deployment
Checklist B Before you deploy an application, certain steps must be completed with no exceptions taken. For instance, such a list may include:
- Code review approval
- Automated and manual testing completed
- Security and vulnerability scans finalized
- Environment readiness assessment
2. Testing Standards
Establish what tests need to be run. Typical examples of common tests may include:
- Unit Testing to verify individual code components.
- Integration Testing to ensure various system components work cohesively.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT), performed by end users to catch usability flaws.
3. Document Requirements
Every deployment should include comprehensive documentation, such as release notes, deployment strategies, rollback plans and the most commonly occurring issues.
4. Approval and Sign-off Process
Specify who has the authority to approve the deployment. This might vary by the complexity of the update, with roles like:
- Project Manager
- QA Lead
- Security Officer
5. Rollback Strategies
A deployment policy would not be complete without providing for rollback strategies in case something goes awry during deployment. Provide steps for undoing modifications should it not proceed as expected.
6. Post-Deployment Monitoring
Make sure that monitoring software and dashboards are used to continuously assess performance after release of an application, and implement measures for responding to any increases in downtimes or errors that arise post release.
Pre-Deployment Requirements
Before an application is accepted to be used It must meet the following requirements:
- Testing:
- All applications should undergo a thorough test, which includes integration, unit, and tests for user acceptance (UAT) depending on the necessary.
- Security Review Security Review:
- A thorough review of security is required by the IT Security Team to ensure that the application isn’t introducing security holes.
- Conformity Checks:
- Your app must be in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations and the internal guidelines, such as privacy laws governing data accessibility standards and any specific regulations for the industry.
- Benchmarks for Performance:
- Your app must achieve performance and scaleability benchmarks established in the Development and QA Teams.
Certification Process
The steps outlined below must be completed in order to achieve certification:
Coding Review:
Every line of code of an application should be thoroughly examined to ensure it complies with best practices in security efficiency, security and maintainability.
Compliance Certification Application Deployment Certification Policy:
To ensure that an application complies with all laws and regulations, its Compliance and Risk Team must inspect it to certify it as compliant.
Security Certification:
The IT Security Team requires security certification of every application they evaluate to verify it has no known vulnerabilities.
User Acceptance Tests (UAT) Application Deployment Certification Policy:
A focused group of users should test your application to make sure it fulfills business requirements while remaining user-friendly.
Performance Certification Application Deployment Certification Policy:
App must pass tests of performance and stress tests in order to confirm its ability to meet anticipated demands.
Deployment Approval Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Once an application fulfills all requirements for deployment by The Application Deployment Team, its deployment is approved.
Post-Deployment Requirements
- Monitoring:
- Post-deployment monitoring should be carried out to ensure that the application is operating as intended. This involves examining for problems with performance, bugs or security flaws.
- Feedback Loop:
- A feedback loop must be in place for users to inform of any issues that arise following deployment. These issues need to be dealt with and resolved quickly.
Continuous Improvement process of deployment is to be reviewed following every release to determine areas of improvement.
Documentation Application Deployment Certification Policy
This Application Deployment Certification Policy ensures that applications deployed into production environments are evaluated, tested, and certified as compliant with security and organizational standards and specifications. Before deployment, each application must undergo stringent performance and functional tests as well as security assessments, in addition to meeting all operational and regulatory compliance standards set by IT Security teams and IT teams. Before deployment can begin, all applications must be approved by both operations and development teams for approval and logged to ensure an audit trail. Infringements to this policy could result in delayed or cancelled deployments – regular reviews will take place to ensure it remains compliant with ever-evolving security needs and business demands.
Compliance Application Deployment Certification Policy
This policy must comply with external organizational standards and regulations that regulate software deployments, including but not limited to:
- Privacy and Data Protection and Privacy (GDPR, CCPA etc)
- Industry-Specific Standards (e.g. HIPAA for healthcare or PCI DSS for payments systems)
- Internal Information Security and Change Management Policies.
Exceptions Application Deployment Certification Policy
Here’s a brief outline of the exceptions for Application Deployment Certification Policy, organized in seven lines.
Critical Applications:
Exceptions can be granted for applications deemed essential to business operations when rapid deployment is necessary.
Regulatory Requirements Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Legal Requirements Deployments required to meet deadlines imposed by laws or regulations could be exempted from certification requirements.
Security Vulnerabilities Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Security Vulnerabilities and Legacy Systems may be eligible to bypass certification procedures.
Legacy Systems:
Patches to address emergency security vulnerabilities might also be implemented without prior certification if necessary. Likewise, legacy applications without certification processes could also be deployed without full certification procedures being followed.
Third Party Dependencies Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Some integrations from third parties do not require full certification if their processes don’t cover this aspect of integration.
Test and Prototyping Application Deployment Certification Policy:
Applications designed to test or prove concepts might not require certification in full.
Time Sensitivities Application Deployment Certification Policy:
If time constraints for deployment are critical, speed of deployment may still be implemented with some restrictions and modifications.
Policy Review
The Application Deployment Certification Policy details the procedures and standards to be observed when testing applications prior to their deployment in production environments. Ensure all applications meet security, performance and conformance standards through rigorous testing and vulnerability analyses. Document the deployment plan, rollback procedures and gain approval from stakeholders. Certification involves sign-offs and cross-functional reviews designed to minimize operational risk. Failure to adhere to certification requirements could delay deployment or lead to rollbacks; thus the policy encourages continued monitoring after deployment to address unexpected issues that may arise. Each team is also required to keep records of certifications they have earned for audit purposes.
Future-proofing Application Deployment Certification Policy
An application deployment policy is more than a mere document; it represents your commitment to security, quality, and efficiency. No matter if you’re running a small start-up or a large enterprise implementing an effective certification policy now can save time, money and build your reputation both now and in the future.
A strategic policy allows teams to focus on innovation instead of fighting fires, leading your business to achieve scalable and sustainable growth.
Have you evaluated your own deployment process recently? Use this guide as a source of knowledge and set off on a seamless and trouble-free experience.
Reference About Application Deployment Certification Policy
1. Canadian Government Email Policy
The Canadian Government provides specific guidelines and policies governing the use of email systems across its departments. These guidelines ensure proper management of government communications, data security, and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Source: Government of Canada Email Policy
2. Amazon Web Services (AWS) Email Policy
AWS provides policies for cloud-based email services, including WorkMail. These policies cover aspects such as data storage, security, privacy, and incident response related to email communications.
Source: AWS WorkMail Policy
3. Google Workspace (G Suite) Email Policy
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) includes policies for email management, including guidelines for security, email encryption, spam protection, and compliance with global data protection regulations like GDPR.
Source: Google Workspace Email Policy
4. Microsoft Office 365 Email Policy
Microsoft provides policies for email management within Office 365, ensuring compliance with security standards, data retention, and privacy laws. These policies help organizations manage email communications securely.
Source: Microsoft Office 365 Email Policy
5. UK Government Email Policy
The UK Government’s digital services include comprehensive policies on email management, email security, and the use of email for government communication, which are structured within the G-Cloud framework.
Source: UK Government Email Policy
6. Oracle Cloud Email Policy
Oracle provides policies for email management under its cloud services. These policies focus on data security, email encryption, user access, and compliance with international laws such as GDPR.
Source: Oracle Cloud Email Policy
7. Australian Government Email Policy
The Australian Government has set policies around cloud services, including email hosting. These policies provide guidelines on email retention, access, and security to ensure proper handling of sensitive government communications.
Source: Australian Government Email Policy
8. Telstra Email Policy (Australia)
Telstra offers guidelines for email use and security as part of its cloud and telecom services. Their policies ensure compliance with data protection laws and secure email communication for businesses.
Source: Telstra Email Policy
9. NEPRA Email Policy (Pakistan)
NEPRA’s policies cover email security and data privacy in communications within the energy sector. This includes guidelines on email retention, encryption, and incident handling.
Source: NEPRA Email Policy
10. PTCL Email Policy (Pakistan)
PTCL provides email services with policies governing email access, usage, security, and retention. These policies ensure the proper handling of business email communications for organizations using PTCL services.
Source: PTCL Email Policy