Introduction
Article summary An email policy is a fundamental strategy to safeguard that email communication within the business is professional, secure and effective. E mail communication is the cornerstone of today’s business transaction, linking employees with staff, customers and other third parties. By instituting a company-wide email policy, you ensure that all communications, including introductions and messages, are delivered politely, clearly, and in an orderly manner. Over here this is who issues the emails; HR/Customer service/Management etc. It also describes the information to be included in introductions such as one’s role, knowledge and reason for communicating. All in all, it’s an excellent way to be clear, respectful, and professional over email.
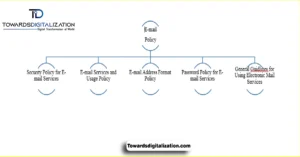
Objectives of an Email Policy
Objectives of an email policy The overall goals of an email policy are to protect messages filed by securing them. Enforcing compliance and enhancing professionalism. The goal is to help get a structure into complex messaging threads (transactional, promotional, marketing) associated with transactional communications. It also appoints roles to various teams on keeping email under control, while preserving privacy.
Through the creation of common benchmarks, it guarantees a degree of consistency that transcends various locales like Pakistan, USA, UK and around the world. Another important goal is to protect against unauthorized access of special information that has been sent through an email. Ultimately, at the end of the day, it promotes an open communication culture — one that not only helps build relationships within your organization but also strengthens connections outside of it.
Purpose of Email Policy
An email policy is established to indicate the acceptable use of sending and receiving e-mails in an organization. For a program like Towards Digitalization this means the people email applying all staff, contractors and partners/visitors.This policy protects the professional, private, and secure communications that the community expects. It covers business emails for customer relations, email marketing campaigns, transactional emails and customer support. Furthermore, the policy requires compliance with local, national and international data protection legislation. By this way, it assures that a continuous legal and healthy communication is preserved.
Internal Email Introductions
Email introductions within your company are important in building up teamwork and togetherness. These emails typically share information about the department, the colleague’s position and the extent of collaboration. They should also mention any applicable expertise or information and facts with which to aid collaborative work. By setting expectations, I am sure these emails help make a clear purpose of the introduction among colleagues. A good internal introduction leads to stronger professional relationships and less friction in working relationships. So the address should be formal, polite and cordial, without being too casual.
External Email Introductions
External intro emails are crucial for building relationships with clients and external stakeholders. Emails of that type should clearly indicate the role for the person, their expertise and a reason for the intro. They can also feature information for business objectives, services provided and expected partnership. This allows recipients to know the context and purpose of the transmission. In addition, these emails need to be professional and polite, that expresses respect and trust. Through adherence to this framework, ministries can enhance engagement with their external stakeholders.
Roles and Responsibilities
The strength of either Email policy is in articulating the roles of Admins, Marketing, Customer Support and Compliance as well as Users. Email administrators work on account provisioning, policies and security. The sales or marketing team ensures promotional emails comply with privacy laws as well as reach relevant contacts. Support teams process transactional messages, confirmations and inquiries in an accurate and timely manner. Compliance Teams track compliance with regional and global privacy laws to secure handling of sensitive information. Finally, you are solely responsible for the content and accuracy of all information contained in emails which you send.
Email Security Measures
Another very important job of an email policy is to retain the security and integrity of your incoming and outgoing email – ensuring that it supports your company’s confidential information. You should encrypt emails that contain sensitive information to prevent unauthorized reading. Security : Control who can email to prevent unauthorized users from sending emails. Virus Protection Scanning and Computer Malware is Crucial to Protect Circle of Life Computers from Cyber-criminal Attacks. Continuous monitoring is the mechanism that enables adequate security controls and alerts for possible breaches. “It’s how you ensure that your data continues to be absolutely valid and also keep the trust with your staff and with those who are watching outside, i.e. stakeholders.”
Email Content Guidelines
Content of email must be professional and follow organization email format. You may write your email in a direct manner that does not add any unnecessary words or other informations about purpose of communication. Your internal emails should offer the right context (both department and role specific). Outbound emails need to bring into focus business objectives, services and the intention to work together. You must maintain a formal tone to ensure clarity, courtesy, and an appropriate level of brevity.
Email Etiquette
Email Courtesy Etiquette: A Thing Of The Past? Employees should not shake hands with the press, use titles (Mr, Mrs) or be rude to them. Emails need to be brief as well, get to the point IF an additional detail wasn’t specified. Professionalism is key, and by forgoing heavy use of all caps, emojis or casual language you can keep that tone. Following etiquettes in communication is very important whether it be verbl, written or the body language. In addition, consistency leads to a good impression in the eyes of your organization and even help you work better with other professionals.
Confidentiality and Privacy
An email exchange between corporates should be a private and confidential communication. Policies As more strains of malware emerge, policies must be in place protecting sensitive information from financial data to client records and proprietary knowledge. Furthermore, privacy, user-friendly email systems, and authentication processes are crucial. Accordingly, it is the responsibility of employees to verify email addresses and handle proprietary messages appropriately.Both GDPR, CCPA and PDPA must be strictly respected. Organizations plan for and prioritize confidentiality in order to limit the damage and preserve trust in professional dialog.
Retention and Archiving of Emails
Email retention and archiving best practices of how we keep business communications on record, but safe for a short amount of time. Emails with legal, transactional or business-critical information are often subject to regulatory retention. Archive or dispose of messages that are not required to save space and resources and keep the system snappy and efficient. Retention policies help enterprises take control of their storage resources and comply with data protection laws. Furthermore, periodic email audits and reviews help maintain accountability. Ultimately, a well-executed retention platform enhances both operational efficiency and legal compliance.
Compliance with Legal Regulations
Email regulations must fit within the legal framework to keep organizations and users from breaking laws. European users are subject to GDPR, U.S. users are under CCPA. Pakistan’s PDPA means that local compliance with data protection is guaranteed. They need to offer explicit instructions for how employees should deal with sensitive information and legal requests. Sanctions for non-compliance, and protocols to report violations, should also be specified in policies. Compliance ensures and then protects an organization’s reputation; it also wards off legal issues and it sets the standard for ethical email practices worldwide.

Managing Retention Policies in Outlook
How to maintain email retention in Outlook Helps you meet your corporate and legal obligations. Users can go to account settings, if allowed, in the desktop app to edit retention policies. Outlook Web Access also supports per-folder retention policies. Exchange or Office 365 administrators can create or edit retention policies for all users from the Microsoft 365 Admin Center. In essence, retention management ensures that emails are either retained or deleted in a consistent manner. Consequently, this allows organizations to remain compliant while effectively managing data storage.
Protecting Against Phishing and Spam
Email use policies need to mitigate threats from phishing and spam to protect staff and all the data that organizations can’t do without. Staff must be alert to suspicious emails, attachments and links. Be sure to establish what the protocol is on reporting phishing attempts to IT or security teams in policy guidelines. It increases resistance using anti-spam filtering, checking systems and encrypted communications. Security measures are strengthened through awareness campaigns and regular updates. Therefore, following these policies will decrease the risk of cyber threats and also secure emails.
Password and Authentication Guidelines
Passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are the core of email security. Email accounts must have a password of at least 12 characters, containing upper and lower case letters, numbers and special characters. You need to change passwords regularly and avoid reusing them. MFA adds another level of security to help prevent unauthenticated access to sensitive accounts. Workers also are not to use info that can easily be guessed, like their name or birth date. Moreover, compliance with these measures ensures user protection and minimizes the risk of any email-related security compromises.
Conclusion
Well-defined roles of use, privacy rules, security and etiquette control the protection of your organization’s information and contribute to productive collaboration. Educating staff on what constitutes a threat, such as-phishing or malware, creates a safer communication landscape. Policies deliver the same level of guidance across regions and departments in terms of legal compliance as well. A Good Email Policy = Protection for Your Organization’s Reputation, Trust-building with Stakeholders, and a Great Return on Time Invested in Communication Ultimately, an effectively written email policy protects your organization’s reputation, builds trust with stakeholders and leads to more efficient communication.
FAQs
Q 1. So why do you need are there email policies?
An email policy establishes the rules of usage for emails in a company. It facilitates professional conversation, guards sensitive data, and supports institutions with complying to privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA and PDPA. It sets out responsibilities, job descriptions and proper use of e-mail.
Q 2. Who is tasked with email security and compliance?
Email admins, marketers, customer support and compliance all have a job to do. Specifically, admins oversee account creation and security, marketing handles promotional emails, customer support manages transactional emails, and compliance ensures that we remain fully aligned with legal requirements.
Q 3. What are dos in email etiquette for the handling of private or sensitive information/ data?
Confidential emails shall be encrypted and transmitted to only to the addressees authorised by Ontime. Staff should check email addresses before hitting send and adhere to company cyber protocols. Moreover, secure data protection ensures privacy compliance while preventing unauthorized access.
Q 4. How long are emails kept and stored?
The company can keep emails for as long as its retention policy allows and legal requirements mandate. You can keep transactional or legal emails in the short term and move all other emails into an archive—literally, if necessary. You must keep regular reviews to follow your guideline and manage the data ideally.
Q 5. What can employees do to avoid becoming a victim of phishing and spam?
Staffs must familiarize themselves with unusual mails, refrain from clicking on unknown links or attachment, and report phishing attacks to the IT of security personnel. Spam filters should be put in place, as well as encryption and training for staff to reduce vulnerabilities and maintain email security.








